Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature
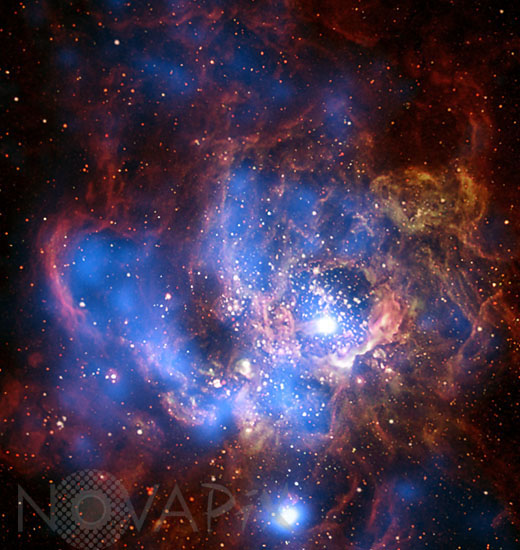

NGC 604 star forming nebula
author: Nasa/CXC/Cfa/ Stsci/Novapix
reference: a-neb06-04002
Image Size 300 DPI: 25 * 27 cm
NGC 604, is one of the largest known seething cauldrons of star birth in a nearby galaxy. NGC 604 is similar to familiar star-birth regions in our Milky Way galaxy, such as the Orion Nebula, but it is vastly larger in extent and contains many more recently formed stars. This monstrous star-birth region contains more than 200 brilliant blue stars within a cloud of glowing gases some 1,300 light-years across, nearly 100 times the size of the Orion Nebula. The bright stars in NGC 604 are extremely young having formed a mere 3 million years ago. The most massive stars in NGC 604 exceed 120 times the mass of our Sun, and their surface temperatures are as hot as 72,000 degrees Fahrenheit (40,000 Kelvin). Ultraviolet radiation floods out from these hot stars, making the surrounding nebular gas fluoresce. NGC 604 lies in a spiral arm of the nearby galaxy M33, located about 2.7 million light-years away in the direction of the constellation Triangulum. The image is a composite of images taken in X-ray (in blue) by Chandra X-Ray observatory and in optical (red and green) by the Hubble space telescope. It shows a divided neighborhood where some 200 hot, young, massive stars reside. Bubbles in the cooler gas and dust have been generated by powerful stellar winds, which are then filled with hot, X-ray emitting gas. Scientists find the amount of hot gas detected in the bubbles on the right side corresponds to the amount entirely powered by winds from the 200 hot massive stars. The situation is different on the left side where the amount of X-ray gas cannot explain the brightness of the X-ray emission. The bubbles on this left side appear to be much older and were likely created and powered by young stars and supernovas in the past.
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved