Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature

European launch vehicles family- Illustration
author: ESA/D.Ducros/Novapix
reference: e-leu12-99802
Image Size 300 DPI: 44 * 43 cm
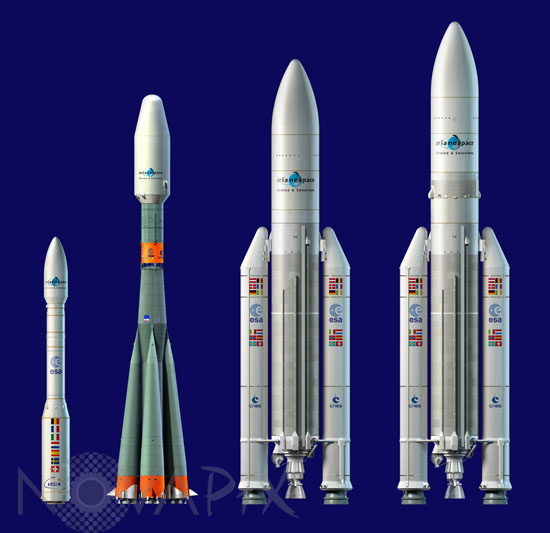
Artist view of the family of launchers to be operated on behalf of ESA from the Guiana Space Center, Europe's Spaceport, in Kourou, French Guiana. From left to right:
Vega, ESA's new small launcher, is designed to loft single or multiple payloads to orbits up to 1,500 km in altitude. Its reference payload capability is about 1,500 kg to a circular 500-km-high Sun-synchronous orbit but it can also loft satellites from 300 kg to more than 2 metric tons, as well as piggyback microsatellites of less than 100 kg each.
Soyuz-ST, the improved version of Russia's Soyuz workhorse launcher with a new digital avionics and a wider, Ariane 4-type payload fairing. A new launch pad is being built in the CSG for Soyuz vehicles.
Ariane 5 ES, another version of the Ariane 5E featuring a restartable version of Ariane 5G's storable propellant upper stage. One of its primary payloads is the Autonomous Transfer Vehicle (ATV) for resupply and reboost missions to the International Space Station.
Ariane 5 ECA, the most powerful version of the Ariane 5E, an evolution of the generic Ariane 5 launcher with an increased propellant load in its solid booster stages and an improved capacity for the liquid oxygen tank of its cryogenic core stage to feed its new Vulcain 2 main engine. The Ariane 5 ECA was first launched on December 11, 2002. Its payload capacity to geostationary transfer orbit reaches 10 metric tons.
Keywords for this photo:
2009 - ARIANE - ARIANE 5 - ARIANE 5 ES ATV - COMPARISON - ESA - EUROPE - ILLUSTRATION - LAUNCHER - ROCKET - SOYUZ - VEGA -
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved