Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature
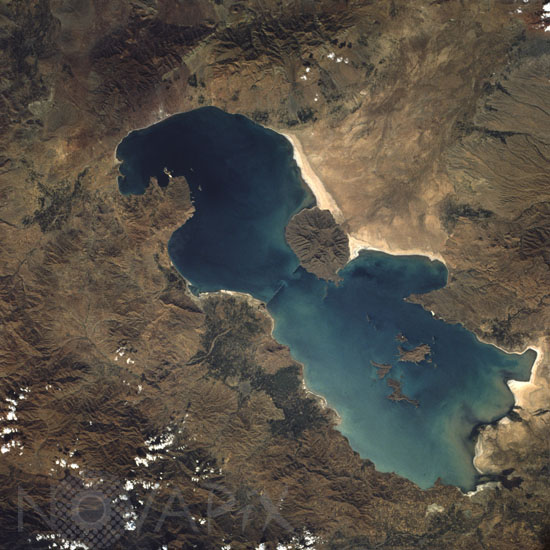

Lake Urmia in Iran seen from space
author: Nasa/Novapix
reference: t-asira-00011
Image Size 300 DPI: 44 * 44 cm
Lake Urmia is an isolated lake in Azerbaijan Province in northwest Iran. The total area of the lake is 1815 square miles (4700 square kilometers), and the north-south length is about 90 miles (145 kilometers). The maximum depth of the shallow, saline lake is approximately 50 feet (15 meters). Climatically, the lake region is located in a semiarid, almost desert environment, with general precipitation averaging 12 inches (30 centimeters) per year. Topographically, the entire region is either plateau or mountain. The surface of the lake is approximately 4100 feet (1250 meters) above sea level with several of the individual volcanic peaks reaching more than 7000 feet (2134 meters) above sea level. The massive, rugged mountain range west of the lake has ridges that exceed 11 000 feet (3353 meters) above sea level. Agricultural patterns are visible in several delta areas around the lake (darker signatures). Sediment patterns can be seen along the southern end of the lake near the salt flats and the delta areas. The highly reflective area along the eastern shore of the lake appears to be either the development of salt deposits along the shoreline or the receding water level in the lake, which exposes more shoreline. The narrow linear features jutting into the lake from opposing shorelines (toward the middle of the lake) could not be identified, but appear to be manmade. Image taken from the space shuttle Challenger in october 1984.
Keywords for this photo:
1984 - ASIA - EARTH - EARTH FROM SPACE - IRAN - LAKE - Lake Urmia - SALT - SALT LAKE - STS-41-G - UNESCO - WATER -
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved