Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature
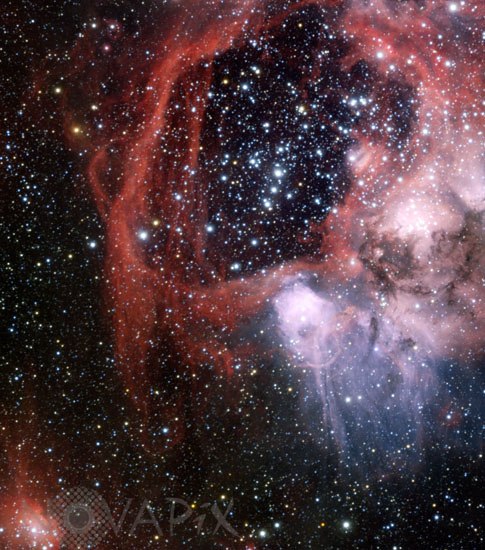

N44 nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud
author: ESO/Novapix
reference: a-neb80-44004
Image Size 300 DPI: 15 * 17 cm
ESO’s Very Large Telescope captured this striking view of the nebula around the star cluster NGC 1929 within the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of our own Milky Way. A colossal example of what astronomers call a superbubble dominates this stellar nursery. It is being carved by the winds from bright young stars and the shockwaves from supernova explosions.
This nebula is officially known as LHA 120–N 44, or just N 44 for short. Hot young stars in NGC 1929 are emitting intense ultraviolet light and causing the gas to glow. This effect highlights the aptly-named superbubble, a vast shell of material around 325 by 250 light-years across. For comparison, the nearest star to our Sun is just over four light-years distant.
The N 44 superbubble has been produced by the combination of two processes. Firstly, stellar winds — streams of charged particles from the very hot and massive stars in the central cluster — cleared out the central region. Then massive cluster stars exploded as supernovae creating shockwaves and pushing the gas out further to form the glowing bubble. Although the superbubble is shaped by destructive forces, new stars are forming around the edges where the gas is being compressed. Like recycling on a cosmic scale, this next generation of stars will breathe fresh life into NGC 1929.
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved