Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature
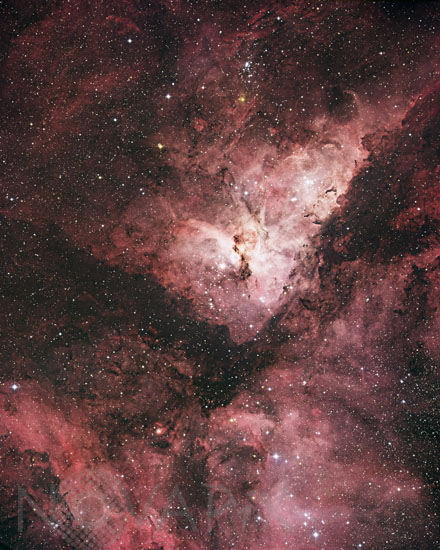

The Carina nebula, NGC 3372
author: Anglo-Australian Observatory/David Malin Images/Novapix
reference: a-neb33-72004
Image Size 300 DPI: 40 * 51 cm
The brightest part of the Milky Way, as seen by the unaided eye, lies in the southern constellation Carina. Here there are an unusually large number of young, hot stars. Their radiation is rich in energetic ultraviolet light. Many of these stars were born within the spectacular Carinae nebula, seen here. The nebula is a cloud of glowing gas composed mostly of hydrogen. It excited by ultrviolet light from the embedded stars. This dostictive emission radiation is responsible for the red colour. About a quarter of the nebula is made of helium gas, the second most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen, and all the other chemical elements account for only a few percent of the total mass. The brightest star in the nebula is known as eta Carinae. This remarkable object is one of the most luminous and most massive stars known.
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved