Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature
Unusual volcanic edifice on Venus
author: Nasa/JPL/Novapix
reference: a-ven06-00046
Image Size 300 DPI: 13 * 12 cm
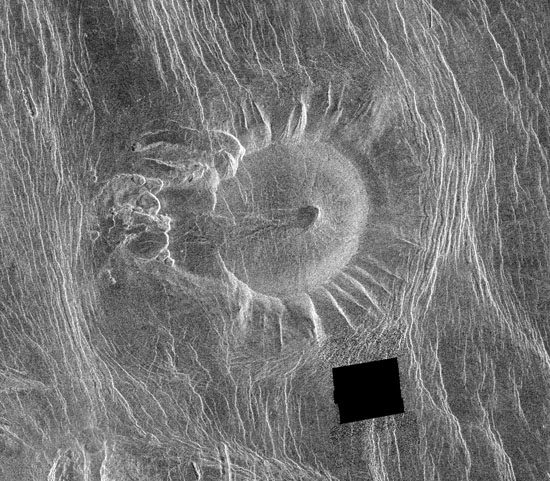
Venus in the southern hemisphere and is centered at 5.5 degrees east longitude, 18 degrees south latitude. It is 122 kilometers (76 miles) across east to west and 107 kilometers (66 miles) north to south. North is at the top of the image. Shown is an unusual volcanic edifice unlike all others previously observed. It is approximately 66 kilometers (41 miles) across at the base and has a relatively flat, slightly concave summit 35 kilometers (22 miles) in diameter. The sides of the edifice are characterized by radiating ridges and valleys that impart a fluted appearance. To the west, the rim of the structure appears to have been breached by dark lava flows that emanated from a shallow summit pit approximately 5 kilometers (3 miles) in diameter and traveled west along a channel approximately 5 kilometers wide and 27 kilometers (17 miles) long. A series of coalescing, collapsed pits 2 to 10 kilometers (1.2 to 6.2 miles) in diameter are located 10 kilometers (6 miles) west of the summit. The edifice and western pits are circumscribed by faint, concentric lineaments up to 70 kilometers (43 miles) in diameter. A series of north northwest trending graben are deflected eastward around the edifice; the interplay of these graben and the fluted rim of the edifice produce a distinctive scalloped pattern in the image. Several north northwest trending lineaments cut directly across the summit region. This peculiar volcanic construct is located 25 to 30 kilometers (15 to 19 miles) north of Alpha Regio, a highly deformed region of tessera terrain. A collection of at least six similar volcanoes has been observed near Thetis Regio, a region of tessera within Aphrodite Terra. Thus, these unusual constructs tentatively appear to be spatially associated with regions of tessera. A tessera is a complex, deformed terrain on Venus consisting of at least two sets of intersecting ridges and troughs. The implications of this spatial association on the unusual morphology of these constructs are being investigated.
Keywords for this photo:
1991 - ASTRONOMY - BLACK AND WHITE - EISTLA REGIO - MAGELLAN - PLANET - RADAR - VENUS - VOLCANO -
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved