Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature
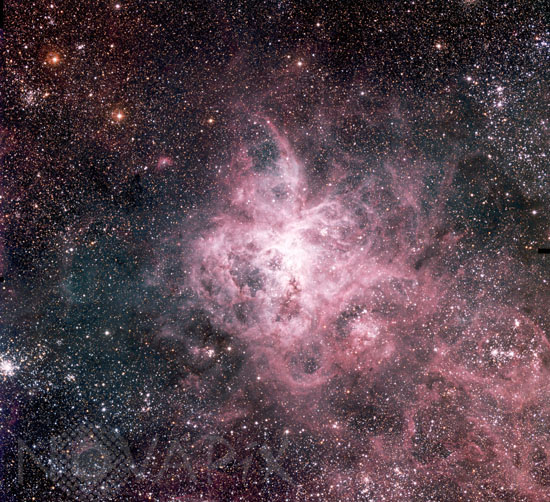

The Tarantula Nebula
author: ESO/Novapix
reference: a-neb20-70001
Image Size 300 DPI: 38 * 34 cm
The largest emission nebula in the sky, the Tarantula Nebula (also known as NGC 2070 or 30 Doradus ) is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) , one of the satellite galaxies to our own Milky Way system. Seen far down in the southern sky at a distance of about 170,000 light-years, this beautiful nebula measures more than 1000 light-years across and extends over more than one third of a degree, almost, but not quite the size of the full moon. It received its descriptive name because of the unusual shape.
It is a splendid object with a central cluster of hot and luminous young stars that powers strong emission from hydrogen and oxygen gas, making the Tarantula Nebula an easy and impressive target for observations, even with the unaided eye. This image of the Tarantula Nebula was obtained with the Wide-Field Imager (WFI) on the MPG/ESO 2.2-m telescope at the La Silla Observatory.
It is a splendid object with a central cluster of hot and luminous young stars that powers strong emission from hydrogen and oxygen gas, making the Tarantula Nebula an easy and impressive target for observations, even with the unaided eye. This image of the Tarantula Nebula was obtained with the Wide-Field Imager (WFI) on the MPG/ESO 2.2-m telescope at the La Silla Observatory.
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved