Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature
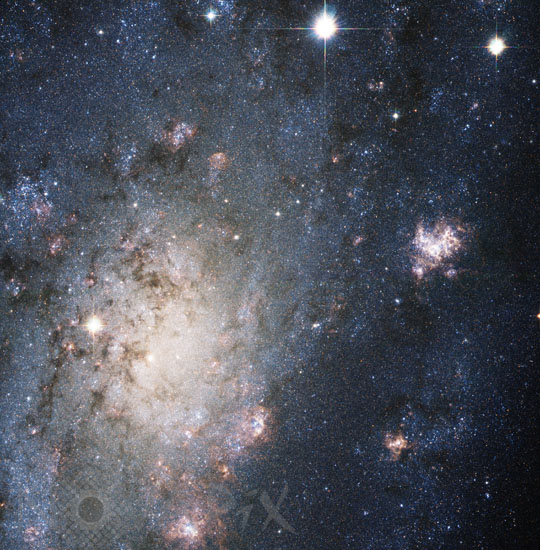

Supernova Sn 2004dj in galaxy NGC 2403
author: Nasa/ESA/Novapix
reference: a-snv02-00401
Image Size 300 DPI: 33 * 33 cm
The explosion of a massive star blazes with the light of 200 million Suns in this NASA Hubble Space Telescope image. The supernova is so bright in this image that it easily could be mistaken for a foreground star in our Milky Way Galaxy. And yet, this supernova, called SN 2004dj (top right), resides far beyond our galaxy. Its home is in the outskirts of NGC 2403, a galaxy located 11 million light-years from Earth. Although the supernova is far from Earth, it is the closest stellar explosion discovered in more than a decade. The star that became SN 2004dj may have been about 15 times as massive as the Sun, and only about 14 million years old. (Massive stars live much shorter lives than the Sun; they have more fuel to "burn" through nuclear fusion, but they use it up at a disproportionately faster rate.) The large number of massive stars in NGC 2403 leads to a high supernova rate. Two other supernovae have been seen in this galaxy during the past half-century. The heart of NGC 2403 is the glowing region at lower left. Sprinkled across the region are pink areas of star birth. The myriad of faint stars visible in the Hubble image belong to NGC 2403, but the handful of very bright stars in the image belong to our own Milky Way Galaxy and are only a few hundred to a few thousand light-years away. This image was taken on Aug. 17, two weeks after an amateur astronomer discovered the supernova. Japanese amateur astronomer Koichi Itagaki discovered the supernova on July 31, 2004, with a small telescope. Additional observations soon showed that it is a "Type II supernova," resulting from the explosion of a massive, hydrogen-rich star at the end of its life.
Keywords for this photo:
2004 - ACS - ASTRONOMY - CAMELOPARDALIS - EVOLUTION - GALAXY - HST - HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE - NGC 2403 - SN 2004DJ - SPIRAL GALAXY - STAR - SUPERNOVA - TYPE II -
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved