Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature
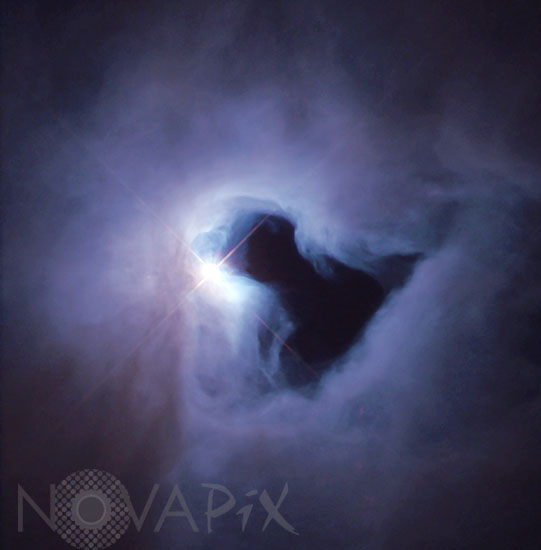

NGC 1999 nebula in Orion
author: Nasa/Hubble heritage team/Novapix
reference: a-neb19-99001
Image Size 300 DPI: 6 * 6 cm
NGC 1999 is an example of a reflection nebula. Like fog around a street lamp, a reflection nebula shines only because the light from an embedded source illuminates its dust; the nebula does not emit any visible light of its own. NGC 1999 lies close to the famous Orion Nebula, about 1,500 light-years from Earth, in a region of our Milky Way galaxy where new stars are being formed actively. The NGC 1999 nebula is illuminated by a bright, recently formed star, visible in the Hubble photo just to the left of center. This star is cataloged as V380 Orionis, and its white color is due to its high surface temperature of about 10,000 degrees Celsius (nearly twice that of our own Sun). Its mass is estimated to be 3.5 times that of the Sun. The star is so young that it is still surrounded by a cloud of material left over from its formation, here seen as the NGC 1999 reflection nebula. The WFPC2 image of NGC 1999 shows a remarkable jet-black cloud near its center, resembling a letter T tilted on its side, located just to the right and lower right of the bright star. This dark cloud is an example of a "Bok globule," named after the late University of Arizona astronomer Bart Bok. The globule is a cold cloud of gas, molecules, and cosmic dust, which is so dense it blocks all of the light behind it. In the Hubble image, the globule is seen silhouetted against the reflection nebula illuminated by V380 Orionis. Astronomers believe that new stars may be forming inside Bok globules, through the contraction of the dust and molecular gas under their own gravity.
Keywords for this photo:
2000 - ACT010210 - ASTRONOMY - BOK GLOBULE - HST - HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE - NEBULA - NGC 1999 - ORION - REFLECTION NEBULA - STAR - STAR FORMATION - YOUNG STAR -
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved