Photo Agency - Astronomy - Space - Nature
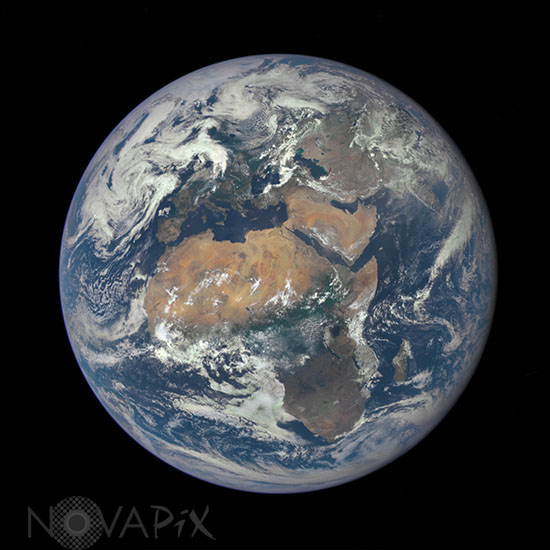

Earth seen by satellite DSCOVR
auteur: NASA/Novapix
référence: t-glb05-00056
Image Size 300 DPI: 17 * 17 cm
The journey has been a long one for the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR). Once known as Triana, the satellite was conceived in 1998 to provide continuous views of Earth, to monitor the solar wind, and to measure fluctuations in Earth’s albedo. The mission was put on hold in 2001, and the partly-built satellite ended up in storage for several years with an uncertain future. In 2008, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), NASA, and the U.S. Air Force decided to refurbish and update the spacecraft for launch.
On February 11, 2015, DSCOVR was finally lofted into space by a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. After journey of about 1.6 million kilometers (1 million miles) to the L1 Lagrange Point, the satellite and its Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) has returned its first view of the entire sunlit side of Earth. At L1—four times farther than the orbit of the Moon—the gravitational pull of the Sun and Earth cancel out, providing a stable orbit and a continuous view of Earth. The image above was made by combining information from EPIC’s red, green, and blue bands. (Bands are narrow regions of the electromagnetic spectrum to which a remote sensing instrument responds. When EPIC collects data, it takes a series of 10 images at different bands—from ultraviolet to near infrared.)
Contact : Stéphane Aubin +33-(0)9-51-26-53-76
© Novapix - All rights reserved